The Autopilot Advantage: 3 Retirement Plan Design Features to Know About

With pension plans on the decline and ongoing questions about the solvency of social security, more and more Americans will need to take action to save for retirement. The SECURE Act and SECURE 2.0 were enacted to help jumpstart those savings or get people back on track. They also provide tax incentives for small businesses that adopt a new retirement plan. But they leave out many existing plans and plan participants who continue to lag behind.
Fortunately, autopilot retirement plan features—auto-enrollment, auto-deferral escalation, and auto-reenrollment—cover many of the provisions mandated by the acts and offer an effective way for participants to boost their savings. And they provide many advantages to your plan sponsor clients as well.
1. Kick-Start Savings with Auto-Enrollment
Auto-enrollment is increasing in popularity because it allows eligible employees to automatically contribute a specific percentage of pay to a retirement plan. According to T. Rowe Price’s recent benchmarking report, plan adoption of auto-enrollment was at 66 percent in 2022. Although there’s an opt-out feature, only 10 percent of employees chose not to enroll.
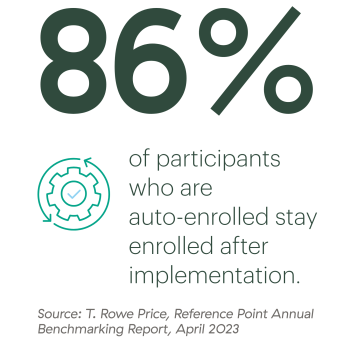
With 86 percent of participants staying enrolled after implementation—compared to just 37 percent participation in non-auto-enrollment plans—it’s easy to see the impact of this simple but effective plan design improvement.
How does this help plan sponsors? There are several advantages:
For firms with 10 or more employees, SECURE 2.0 requires plans adopted after December 31, 2024, to automatically enroll participants as they become eligible. It also provides an annual tax credit of up to $500 in the plan’s first three years for any plan with fewer than 50 employees that adopt auto-enrollment.
Increased participation and higher contribution rates may favorably affect a sponsor’s nondiscrimination testing results, allowing owners and highly compensated employees to contribute more to their retirement savings plan.
By reducing paper-based workflows, employers can onboard new employees more efficiently.
Simplified selection of appropriate investments, particularly target-date fund investments, often fulfills qualified default investment alternative (QDIA) objectives, providing safe harbor protections for plan fiduciaries.
When employees can afford to retire, it benefits them and the business’s financial resources. Enhanced retirement plan offerings are also a great way to attract and retain talent.
2. Save More with Auto-Deferral Escalation
By adding auto-deferral escalation to a plan, participants can incrementally bump up their contribution rates until they meet a predetermined level. The minimum recommended ceiling is 10 percent. Plan sponsors can set the percentage by which a participant’s elective deferral will increase each year (1 percent is most common) until it reaches a predetermined ceiling.
By implementing an opt-out method, more people can save more for retirement. According to T. Rowe Price, 62 percent of participants presented with an opt-out method for auto-deferral escalation remained enrolled, compared to a 10 percent adoption rate for those who had to opt in. Plus, increasing deferral percentages enables participants to realize the full extent of their employer-matching contribution possibilities—no more leaving free money on the table!
3. Hit the Reset Button with Auto-Reenrollment
For participants who aren’t confident in choosing investments or lack time to manage them, reenrollment is a great way to give participants a fresh start and ensure that they’re repositioned to meet their retirement goals. Participants are notified that existing assets and future contributions will be redirected from their existing 401(k) investment choices to the QDIA (typically a target-date fund) on a specified date unless they opt out.
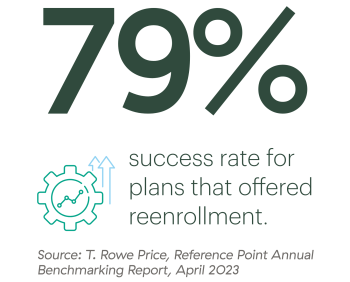
When implemented correctly, reenrollment allows plan sponsors to strengthen their fiduciary standing by gaining favorable QDIA safe harbor protections. While only 14 percent of plans offered reenrollment, the success rate in 2022 was 79 percent.
Getting Your Plan Sponsor Clients on Board
There’s so much to gain from shifting to an automatic retirement plan design. So, how do you get your plan sponsor clients to make the move? Here are some steps you can follow:
Review your book of business. Identify plans that aren’t set up with auto features, and determine who could most benefit from automatic plan design. Those with the most to gain include:
Plans with low or declining participation rates, low or declining savings rates (the average participant savings rate is 7.3 percent, according to Vanguard research), or low average account balances (the average balance is $141,542, according to Vanguard research)
Plans that recently had to make corrective distributions due to nondiscrimination testing failure and required highly compensated employees to have a portion of their elective deferrals returned
Firms with multiple office locations, which typically have enrollment and engagement challenges
Plans that don’t offer QDIA or target-date funds
Present the case. Highlight the benefits and be sure to note how a retirement plan benefit can be a key factor when trying to attract and retain talented employees. Also, consider sharing best practices for each feature.
Auto-enrollment. Suggest setting the default auto-enrollment rate at 6 percent or higher. This is the standard rate for 39 percent of plans, which represents an increase of nearly 100 percent over nine years. For clients whose plans have already adopted this feature at a lower default rate, suggest bumping it up to 6 percent.
Auto-deferral escalation. Encourage clients to use a higher annual increase rate (2 percent rather than 1 percent) and to aim higher with the annual increase cap amount (e.g., 10 percent–15 percent) to align with the rise in auto-deferral escalation ceiling rates. Employers who offer annual pay raises can also target deferral escalations around the same time of year to reduce employee shock.
Reenrollment. Recommend reenrollment as a way to improve participation in the plan, provide professional management of assets, and fulfill their fiduciary obligations. Emphasize the importance of periodically reviewing the plan’s QDIA to ensure that it reflects the plan’s goals and objectives.
Talk with the service providers. Your clients’ service providers (e.g., recordkeepers and third-party administrators) can determine whether the features are feasible for a particular plan and how they may affect the employer’s annual nondiscrimination testing and matching contribution budgets. Additionally, check to see if adopting auto provisions will trigger fee reductions from the recordkeeper.
Now’s the Time to Start the Conversation
The SECURE Act and SECURE 2.0 will benefit many Americans who need to save more for retirement. If you have clients with existing plans, however, they won’t be required to adopt the auto features. That leaves the door open for you to convince them why it’s good for them and their participants. Give your clients the nudge they need today!
Interested in learning how partnering with Commonwealth can help you evolve your retirement plan business? Contact us today.
Editor’s note: This post was originally published in January 2021, but we’ve updated it to bring you more relevant and timely information.
This material is for educational purposes only and is not intended to provide specific advice.
Please review our Terms of Use.
